Rehabilitation pathways
- Four
Pathways - Pathway 1
Person outomces - Pathway 2
Wrap around activites - Pathway 3
Typical settings and services - Pathway 4
Funding
Four pathways
To understand an individuals' client rehabilitation pathway and make it successful it is useful to understand:
- The person's injury and their personal journey of recovery and rehabilitation outcomes
- The rehabilitation core activities/interventions that wrap around the person on their journey
- Typical service settings & pathways through them
- Typical funding pathways for rehabilitation and support services.
A successful rehabilitation process weaves these four strands together into a unified whole.
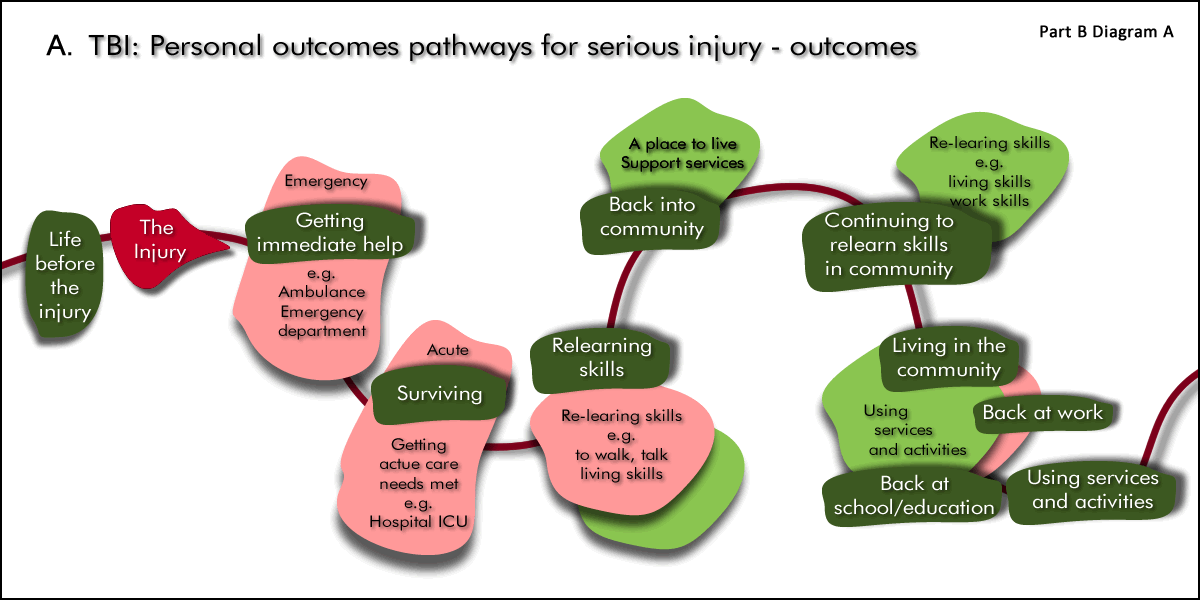
Pathway 1. Injury and personal rehabilitation outcomes pathway
This pathway is unique for every person with a TBI.
The goal is for the person to be independent as they possibly can.
This is a personal outcomes pathway:
To understand the person's recovery and rehabilitation outcomes pathway - it is important to understand:
Their life before the injury AND
The injury and the impairments it causes AND
The wide impacts cause by the impairments AND
The their recovery and rehabilitation pathway of achieving outcomes to address the impairments and impacts - including foe example surviving, relearning skills, etc.
For children with brain injury it is also essential to understand the development of children, their brain and their psycho-social development.
The core legend elements in many of the diagrams are:
Pathway 2. Rehabilitation core activities wrapping around the person
These rehabilitation core activities/interventions wrap around the person on their journey of achieving rehabilitation outcomes.
Brain injury rehabilitation core activities are part of the process of achieving the outcomes for the person with the brain injury (and their family, carers and friends).
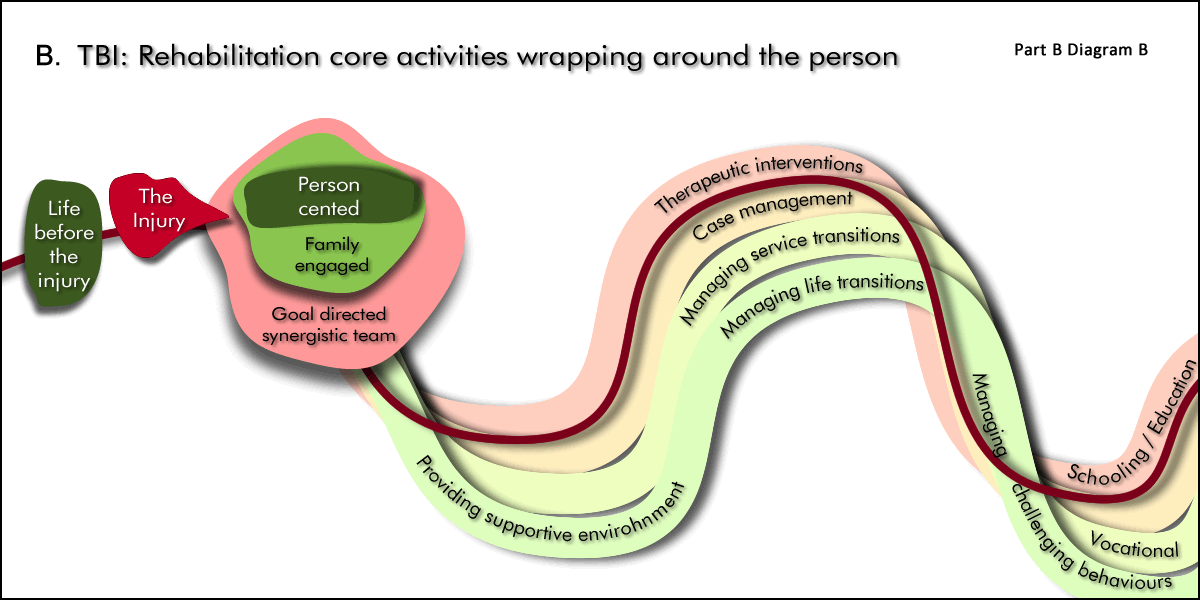
Core activities wrapped around the person include:
Person centred care & goal directed synergistic team
- Person centred care, engagement with family & enabling self-management
- Goal directed synergistic team work where the Team includes the person, family/carers, rehabilitation specialist, clinicians, other services.
Supportive environment
Therapeutic interventions promoting recovery, adaption, compensation and prevention
Managing disorders of consciousness and associated behaviours
Managing life and service transitions
- Managing life transitions well - e.g. child to young person, young person to adult, employed to retired
- Managing transitions from one service to another well including child to adult services
Case Management
Collaborations, Partnerships & Funding
- Managing icare and other insurance funding
- Collaboration with private clinicians
- Collaboration with other health services (e.g. mental health, drug and alcohol)
These core activities take place in a variety of settings including hospitals, home and other accommodation places, community locations, schools, work places.
Pathway 3. Typical settings and services pathway
The exact service pathway will vary from person to person, and will vary from child to adult services.
This is a pathway though settings and services. The availability of services and settings also impacts on the particular pathway for the individual.
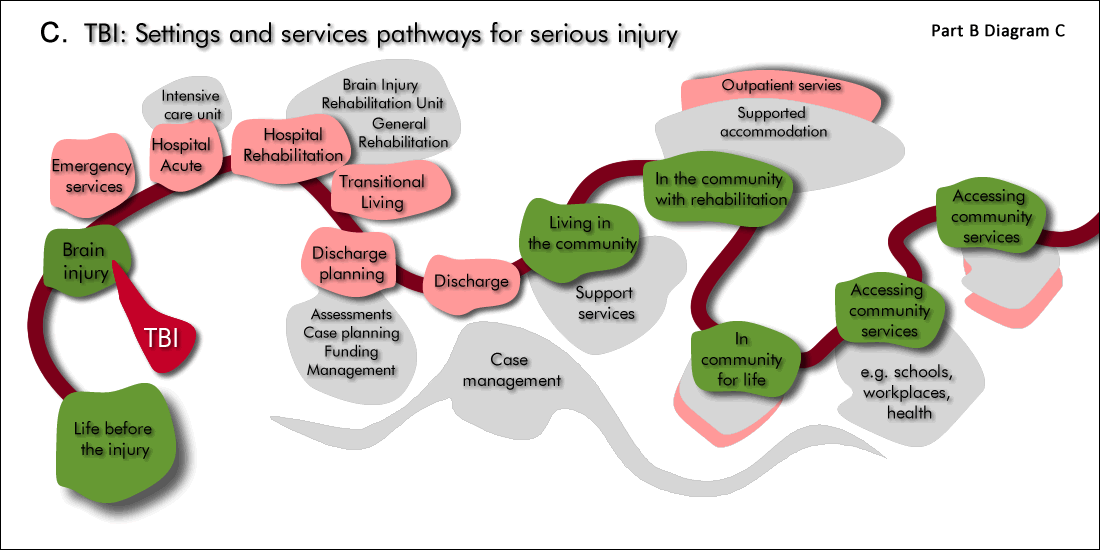
A typical setting and services pathway for severe TBI is:
- The injury event
- Emergency services (possibly including retrieval)
- Hospital acute care (possibly including ICU)
- Hospital rehabilitation
- Transitional care (possibly including Transitional Living Unit)
- Discharge planning and discharge to the community
- Living in the community - often with ongoing rehabilitation and out-patient services
- Vocational rehabilitation (where applicable).
For many people case management is the process that weaves all the threads together through services and settings.
For children a typical service pathway may also include transition from children’s to adult services.
Children’s services also include rehabilitation for schooling/education.
In the community the person could be living independently in their own home, alternatively they could require supports to live in their home and access the community and community services.
Pathway 4. Funding pathways - funds for services
In addition to the funds provide to NSW Health and Local Health Districts for the provision of heath services there are multiple sources of funds that the person may potentially be able to access to pay for the services and supports they require to live independently in the community.
This is a map of some of the more common funding pathways.
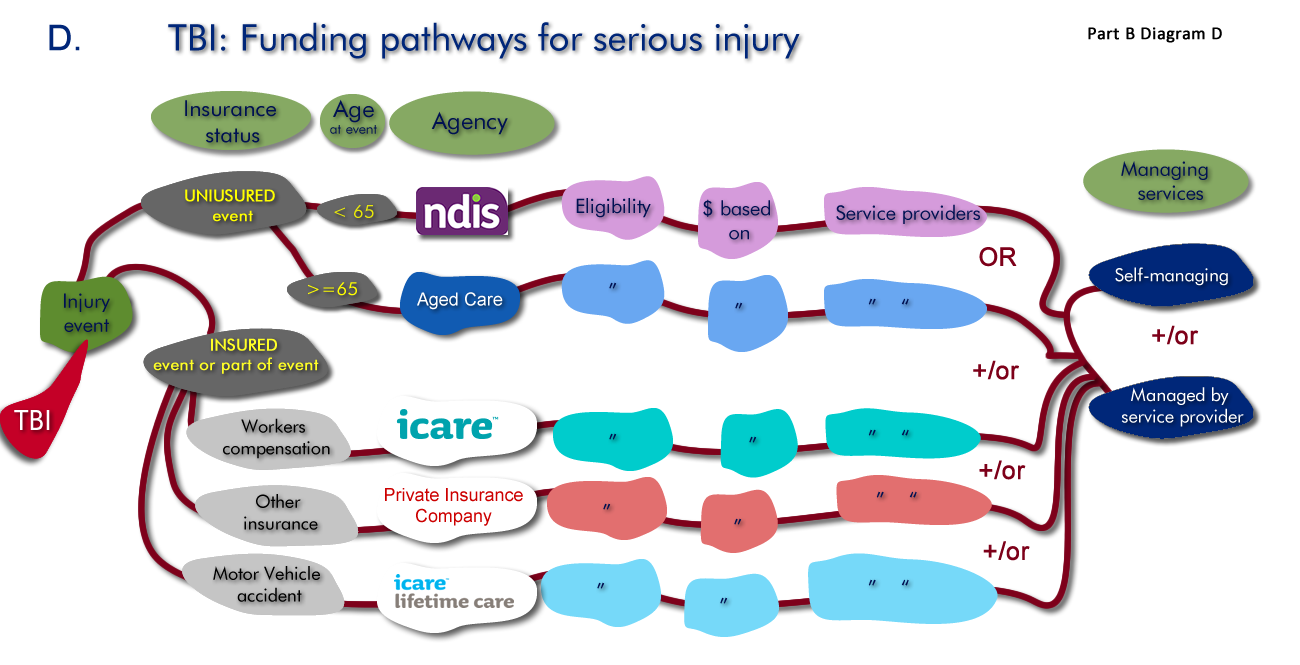
One person can have multiple funding pathways, a person can be eligible for the NDIS, be receiving a workers compensation payment and have private disability insurance.
For each person with a serious TBI the key question is:
What is the insurance status of the injury event and the person's age at the time of the injury and the implications of this?
The insurance status and/or age at the injury event will determine what sources of funds the person is entitled to.
Many injury events are covered by insurance, for example:
- Workers compensation
- Insurance policies such as income insurance, disability insurance, public liability insurance.
- Motor vehicle accident insurance
If the injury event is covered by insurance the person may be entitled to insurance payouts from the relevant insurance.
Irrespective of these insurance payouts people may be eligible for application to the National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) and/or Commonwealth Governments Aged Care Programs including the Commonwealth Home Support Program. Lifetime care participants do not also receive funding from NDIS.
If the age at injury is less than 65 the NDIS applies. If the age at injury is 65 or more the Aged Care Programs apply.