Cause to impact
Cause to impact
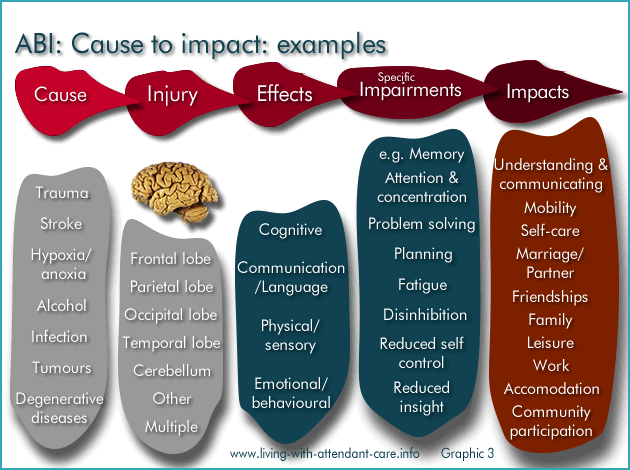
The cause of the ABI makes a physical injury to the brain (in one or more parts of the brain) which in turn has an effect in areas such as cognition, communication and language, etc which can be seen through specific impairments (e.g. memory difficulty, difficulty with problem solving) and these in turn impact on the person's life ( self-care, relationships, work).
Each person with an ABI is different because:
- the exact nature of the injury to the brain is different from one person with an ABI to the next and
- this in turn means the general effects and specific impairments are different from one person with ABI to the next and
- this in turn means the impacts on life of the person with ABI are different from one person with ABI to the next.
Introduction
Common effects of Traumatic Brain Injury include:
- Cognitive
- Communication/language
- Physical/sensory
- Emotional/behavioural/personality
There is overlap and interconnections between these effects. The specific effects will be unique to each individual and their injury. The extent of the effects and challenges for the person with brain injury depends on:
- The severity of the TBI
- The location of the brain damage in TBI
- The length of time since brain injury
- The extent a person has been able to integrate back into the community
- The support available to the person.
Challenges and difficulties
These common effects of TBI create challenges for people with TBI.
Just as the specific effects will be unique to each individual and their injury, the specific challenges will also be unique to each individual and their injury.
Some common challenges and difficulties are:
- Having difficulty in paying attention
- Being easily confused and overwhelmed
- Having problems in learning new information
- Being slower in processing information
- Difficulty in being able to use their knowledge in new situations
- Experiencing difficulty in keeping up with conversations
- Having difficulty in starting activities
- Experiencing word-finding difficulties
- Having problems in producing or understanding language
- Having problems getting or staying organised
- Having problems in planning
- Fixed in thinking patterns
- Difficulty following the social rules and conventions of communication
- Loss of self-esteem and self-confidence
- Changes in personality, egocentric, outgoing/introverted
- Irritability and "short fuse" / increased anger outbursts (very common) / difficulties in emotional control
- "Before/now" comparisons
- Impaired social and personal coping skills
- Impulsivity
- Sexual disinhibition
- Lack of initiative & drive / apathy, low motivational states
- Adjustment issues-depression, anxiety
- Relationship changes